Stratification
Stratification is a tool used to group data, objects or people into separate and distinct categories. Analysis of grouped data can help identify various interesting patterns and relationships that might not otherwise be apparent if presented together.
The word stratification is related to the Latin "stratificationem" and can be understood as "formulation or arrangement in layers".
How to use stratification?
The stratification process consists of several stages:
- Collection of data. Stratification will be possible when data with as many details as possible are collected to group them. For example, when collecting information on product defectiveness, it is useful to additionally collect such details as:
- Product type (symbol, p/n, revision)
- Location (identification of machines, lines, plant)
- Production time (date, work order number, shift)
- Type of problem identified
- Other (e.g., component lots used)
- Determination of stratification criteria. Engineers should determine what criteria they want to divide the data based on. These can be product characteristics (e.g., type, revision), time (production date, shift number) or other relevant parameters.
- Data Breakdown. The data is then segregated according to predetermined division criteria. Each group contains elements with the same or similar characteristics (it is homogeneous). A given result should belong to only one group.
- Analysis. Each group is analyzed separately, using appropriate statistical tools. This allows for a more accurate understanding of the quality in each segment.
- Conclusions and Actions. Based on the analysis, conclusions can be drawn, and specific actions can be taken to optimize quality in specific areas.
Example of stratification
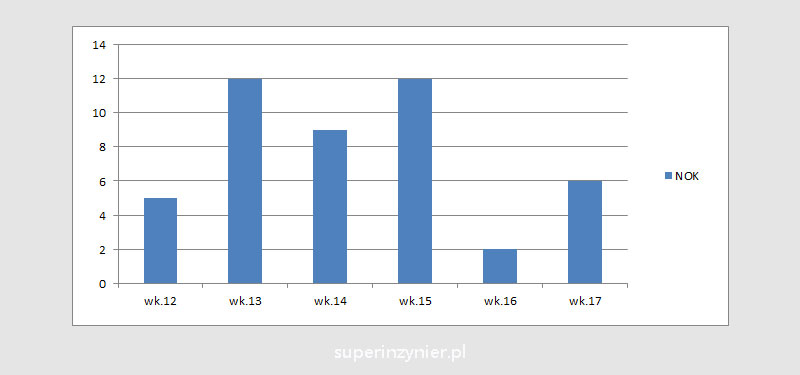
The chart below shows the number of non-conforming products (NOK) shipped from the plant in weeks 12 through 17. The data covers 3 types of products from three production lines.
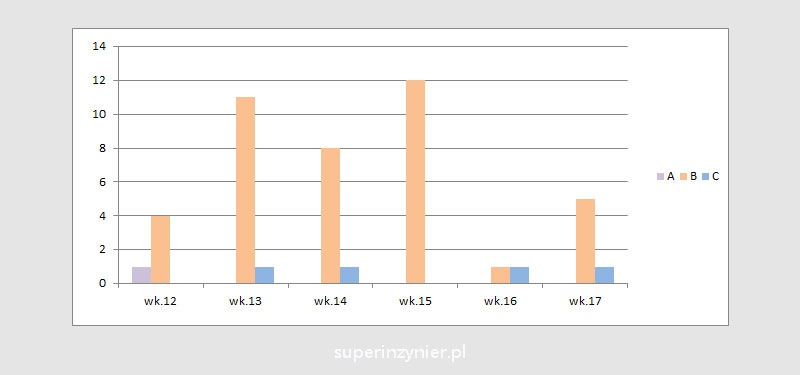
The same data has been stratified. The chart below shows the number of non-compliant products by week, but this time grouped by product type (A, B, C). As you can see, the problem is mainly with product B.
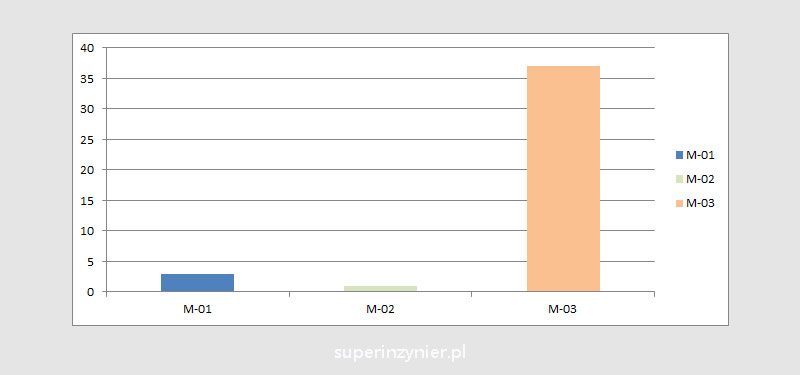
The data regarding the number of nonconforming type B products have been grouped according to the line number on which they were produced. As can be seen, the problems are mainly related to the M-03 line.
Through stratification, we can conclude that corrective actions should be implemented first in the assembly of product B in line M-03.
Stratification and correlation
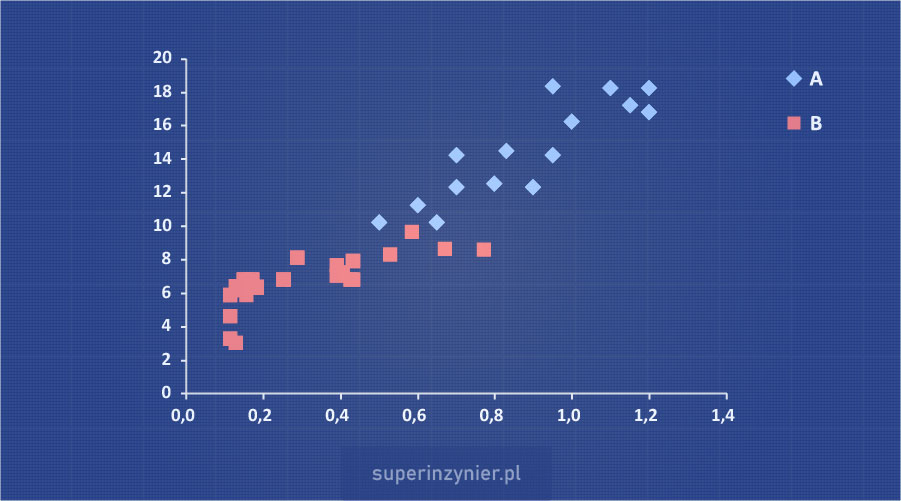
Stratification can be very helpful in analyzing the data presented in the correlation chart. The results on the graph can be shown in different colors or with different labels depending on the category. Example charts:
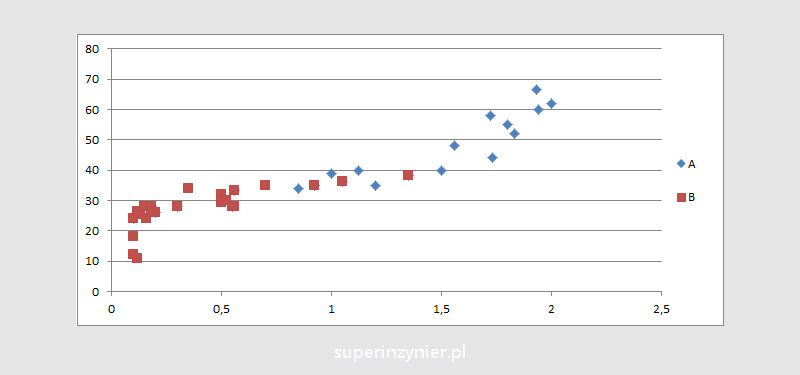
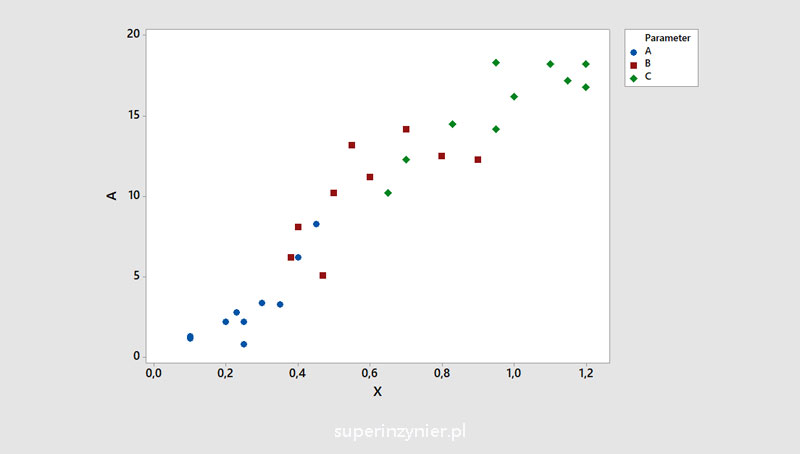
You can read more about the correlation diagram and various aspects related to data analysis in the article: Scatter diagram.
Advantages of stratification
- Stratification allows faster detection of different patterns, which may facilitate identification of the cause of the problem. E.g. defects affect only type B products manufactured only in the M-03 line, which narrows the range of potential causes of the problem.
- Support the data analysis and reporting process. You can present results in relation to various breakdown criteria.
- Faster response to problems. Stratification allows you to see patterns more quickly, so it allows you to react more quickly to problems as they arise.
- Often used as part of problem solving, e.g., the 8D Method or Global 8D (G8D).
- Stratification can be used in any industry.
Disadvantages of stratification
- Requires precise criteria: Proper application of stratification requires precise criteria for division, which can be difficult in some cases.
- Increased workload: The stratification process can be more time-consuming than general data analysis, as collecting and analyzing data for different criteria can be time-consuming.
Summary
Stratification is an important tool in the field of process and product improvement that allows for more precise data analysis. By properly grouping the results, engineers can see different types of correlations (patterns / regularities) and react with the appropriate precision.
Stratification is a tool worth using for a variety of analyses, so when designing a data collection system, consider what details to collect so that you can later use stratification effectively to improve the quality of your processes and products.